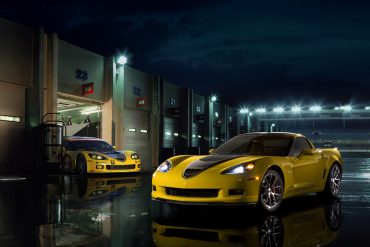
Immediately following this unveiling, consumers began clamoring at the opportunity to become one of the fortunate few to own their own IMSA GTLM Championship C8. Chevrolet filled all 1,000 orders for the race-inspired commemorative C8 in record time, as production commenced. Those lucky enough to place their order before the mandatory production cap was reached, were treated to a handful of IMSA GTLM Championship C8 variants to choose from.
The launch of any new Corvette is significant, and the new-for-2014 C7 model launching this year brings sweeping changes, including upgraded performance and a more contemporary, international styling language. To mark the car’s debut, Chevrolet is prepping the Corvette Stingray Coupe Premiere Edition—and just 500 will be built. While the engine and the transmission options remain unchanged, the Premiere Edition isn’t going to be hard to pick out of a lineup.
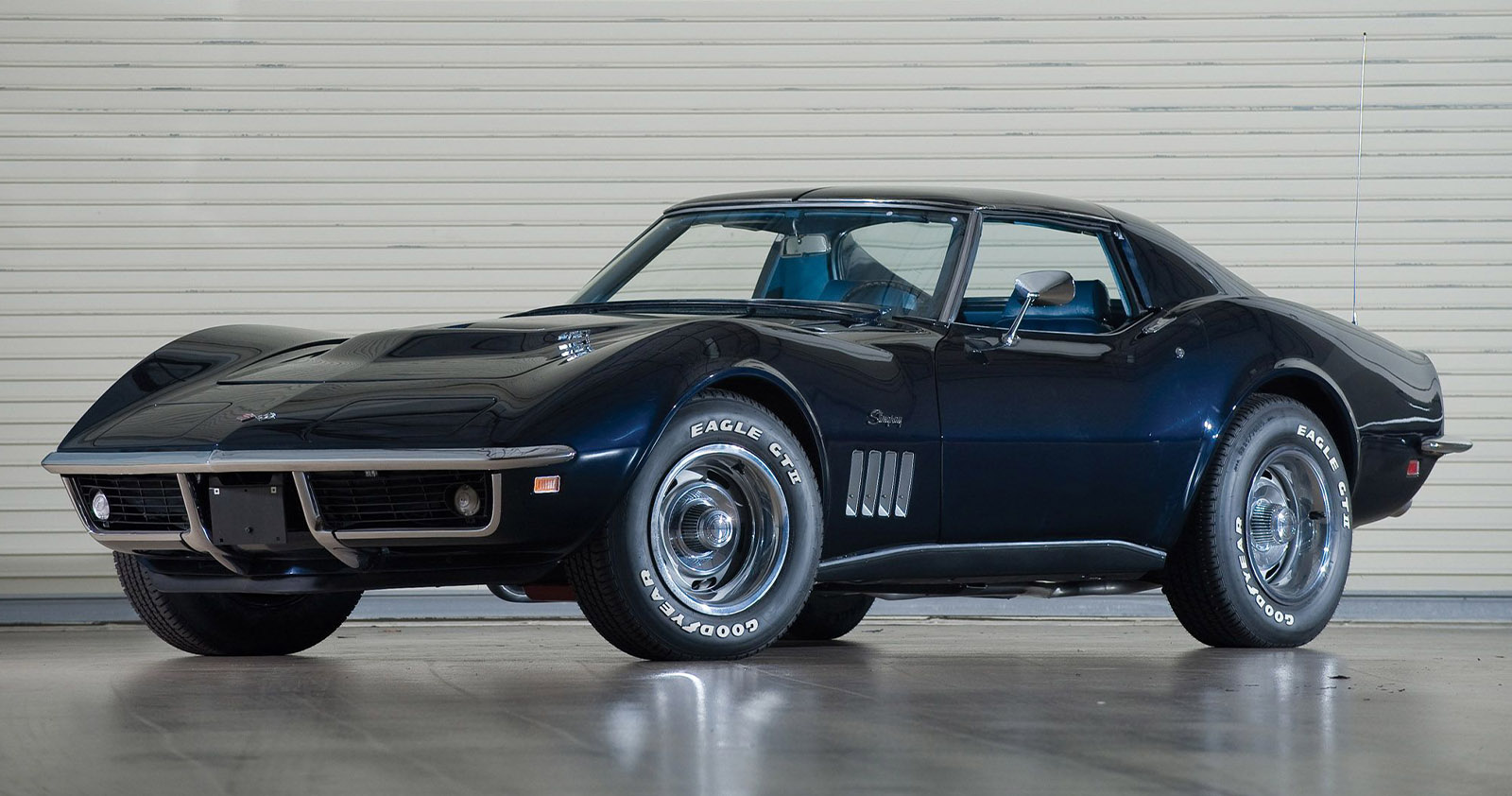
For competition, race customers had a range of options available to them including the N03 36-Gallon Fuel Tank, closer rear axle ratios and the C48 Heater/Defroster Delete (-100). Most cars equipped like this came with either L78 or the L84 with Ram-Jet Fuel Injection.
The Corvette Z06 that served as the Daytona 500 pace car was mechanically identical to those available at Chevrolet dealerships. It was the fastest vehicle ever offered by Chevrolet and General Motors. With 505 horsepower (377 kw) and 470 lb.-ft. of torque (637 Nm) from its 7.0L all-aluminum, racing-inspired engine, the Corvette Z06 leaps from 0-60 mph in 3.7 seconds and has a top speed of 198 mph. The Corvette Z06 Daytona 500 wears a unique paint scheme.
The Purple People Eater MKIII is a 1959 Corvette that was literally unbeatable in SCCA B-Production racing in the late 1950s. There were three Purple People Eaters built in 1958 and 1959. The 1959 model, won every race it entered, except the last one, with Jim Jeffords behind the wheel and mechanic Ronnie Kaplan turning wrenches. The car was built by a team at Nickey Chevrolet in Chicago.
A Chevrolet Corvette Z06 paced the field for the Allstate 400 at the Brickyard on Sunday, July 29 at the Indianapolis Motor Speedway. A Chevrolet has performed pace car duties for all 14 editions of the Allstate 400 at the Brickyard, one of NASCAR's most highly anticipated events since the inaugural in 1994. Also, Chevrolet once again supplied event support vehicles, including Silverado pickup trucks, for on track activities.
There’s a long, rich history between the Chevrolet Corvette and the DeLorean Motor Company (DMC), or at least between GM...
The 2013 Corvette 427 Convertible served double-duty as a commemorative edition model. While it marked the departure of the sixth-generation Corvette, it also...
This one-off 1961 Vignale Corvette was built for the 1961 Salon de l'Automobile in Paris, France. It was based on a 1960 Corvette chassis and built by Italian coachmaker Carrozzeria Vignale. The body was designed by Gordon Kelly.
The “Ron Fellows ALMS GT1 Championship Edition Corvette Z06,” or Ron Fellows Edition for short, stands as the first autographed...
This special edition takes the upgraded handling and appearance that comes with the Grand Sport moniker and adds some special cosmetic touches for extra uniqueness. Along with a stunning gray metallic paint color, it features blue accents that harken back to previous Grand Sports. A representation of the original Grand Sport race car is embossed onto the headrests. Powered by the regular (and excellent) LT1 V-8, it features magnetic ride control, an electronic limited-slip differential, and Grand Sport wheels.
The GS II (Grand Sport II) was a test vehicle completed in late 1963 by Chevrolet Engineering Center (C.E.C.). The chassis was constructed of spot-welded sheet steel and was fitted with narrow tires. With only minor testing done at GM’s test facility in Michigan, the vehicle was shipped to Texas to the Chaparral Cars test facility.
The Specialty Engineering Group (SVE) has partnered with Chevy to create the 2019 Yenko/SC Corvette Stage II. This new Corvette, which is the creation of Specialty Vehicles Engineering in cooperation with Chevrolet, delivers an incredible 1000 horsepower and 875 lb-ft of torque. Better yet, it's an option that you can order from your local Chevy dealership.
The 427 Limited Edition option, code Q8A and Z44, was limited to 505 examples globally with 427 destined for North American customers. As a retirement gift to Wil Cooksey, the Corvette plant manager from 1993 to 2008, he chose the color scheme and hand signed and numbered the underside of the armrest console lids on all 505 examples in which this example is #6. As part of the package, the seats and the floor mats have “427” embroidery, and the center-console trim plate is color matched.
Since the arrival of the eighth-generation Stingray Corvette in 2020, and with it, the arrival of Corvette’s first hard-top convertible,...
Chevrolet introduced the limited production Corvette GT1 Championship Edition at Sebring International Raceway. The GT1 Championship Edition (Regular Production Option GT1) commemorates the success of Corvette Racing and the Corvette C6R.
Throughout its tenure, the Corvette has been the recipient of numerous redevelopments and reconfigurations. As such, the iconic American sports...
While it was understood that the Corvette Indy Concept would never be fully realized as a production vehicle, it paved the way for the creation of the twin-turbo CERV III. The CERV III (Chevrolet Engineering Research Vehicle No. 3) was introduced in January, 1990 at the International Auto Show in Detroit, Michigan. Like the latter iteration of the Corvette Indy Concept car, the CERV III was fitted with a 5.7 Liter, 32-valve, dual-overhead cam LT5 engine that featured twin turbochargers. It had 650 hp and 655 lb/ft of torque and top speed of 225 mph.
This 1961 Chevrolet Corvette factory race car possesses a host of rare options and a provenance worthy of the velvet rope treatment at any of the world’s finest auto museums or vintage races. Gulf Oil sponsored and driven to an SCCA B-Production national championship by the likes of Dr. Dick “The Flying Dentist” Thompson and Don Yenko, it stands as one the most successful and important production-based Corvette race cars ever constructed.
Chevrolet launched the Corvette Centennial Edition to mark its 100th anniversary in 2012. This special package was available across the...
How do you beat a slew of Fox-Body 5.0 Mustangs that seemingly dominated the roads in the late '80s? You take a 454 cu.-in. big-block engine and stuff into a C4 Corvette and call it "Big Doggie". An experimental vehicle used to determine how to convert from a small block to a big block. Its 454 big block V8 along with its orange paint make this high horsepower engineering study a one-of-a-kind standout in Corvette history. The car had as much HP as the '90 ZR-1 did and it was named "ZR-2" or "Big Doggie". Old dog, new tricks joke?
Based on Harley Earl’s Project Opel plaster model, the EX52 / 122 was the original concept car that inspired the nation and left countless consumers wanting a Corvette to call their own. This Corvette concept was introduced at GM’s Motorama in January 1953.
The 1973 Chevrolet XP-898 concept car was built with a frameless fiberglass foam sandwich body and chassis. This two-seater sports coupe offered a unique look at alternative engineering approaches to future techniques in design and manufacturing. The entire body consisted of four lightweight fiberglass outer body panels.
The Vetter Slash, a Corvette-Based Concept Car Although every generation of Corvette has its own, dedicated group of devout enthusiasts/owners,...
In late 2007 Corvette Europe approached the FIA seeking approval to race a C6 Coupe in the GT4 category. After much study the FIA approved their request. Kroymans shipped a new 2008 C6 Z51 six-speed coupe to Callaway Competition in Leingarten, Germany. In less than six weeks the Callaway team stripped the new car of all non-essential parts including carpet and standard seats.
A Corvette in name only, the Corvette GTP (Grand Touring Prototype) was one of the fastest and most exotic race cars ever to wear a red Bowtie. Based on an English Lola T600 chassis and powered by an all-American turbocharged Chevy V6, the mid-engined racer was a rocketship. At full boost, the Corvette GTP's 3.4-liter (209ci) V6 pumped out more than 1,000 horsepower.
Chevrolet developed the Lola T711 as part of an effort to boost the Corvette brand’s visibility in motorsports. While its...
Chevrolet knows their clientele, and with the 1996 Corvette Collector's Edition LT4, the automaker put together a special package that would entice hard-core 'Vette fans with a unique tribute to the outgoing C4 model. The $1250 option brought unique Sebring Silver Metallic paint, 5-spoke wheels, and, of course, special badges and embroidery. It also received the upgraded LT4 powerplant available in the Grand Sport, and with 330 horsepower on tap.
Following its 2015 victories at the Daytona Rolex 24 and Sebring 12 Hours, Chevrolet introduced the 2016 Corvette Z06 C7.R...
The 2013 Corvette 427 Convertible served double-duty as a commemorative edition model. While it marked the departure of the sixth-generation Corvette. The real selling-point was the powerplant at the heart of the car - a 427-cubic-inch (7.0L) LS7 engine, the same engine used in the C6 Corvette Z06. Rated at 505 horsepower (377kW) and 470lb.-ft of torque (637 Nm), this 427 was the most powerful engine GM had ever installed in a production Corvette convertible to date.